Brake Pad Introduction
■ Brake pads, also known as brake linings, are the most critical safety components in the automobile brake system. The effectiveness of the brakes largely depends on the performance of the brake pads, Typically, brake pads consist of a steel plate. a bonding insulation layer and a friction block. The insulation layer, made of non-heat-conducting materials, serves to insulate heat. The friction block, composed of friction materials and adhesives, is pressed against the brake disc to generate friction during braking, thereby slowing down or stopping the vehicle.
■ The friction material of TOMOI Disc brake pads is R&D patent of the engineers in at Japanese Headquarters.
■ TOMOI Disc brake pads rely on high braking efficiency. which can be achieved by balanced heating and heat dissipation of the brake pads in different operating modes, thereby ensuring the stability of product quality, effectively reducing the noise of the brakes and discharging the dust generated by the friction between the brake pads and the brake disc.
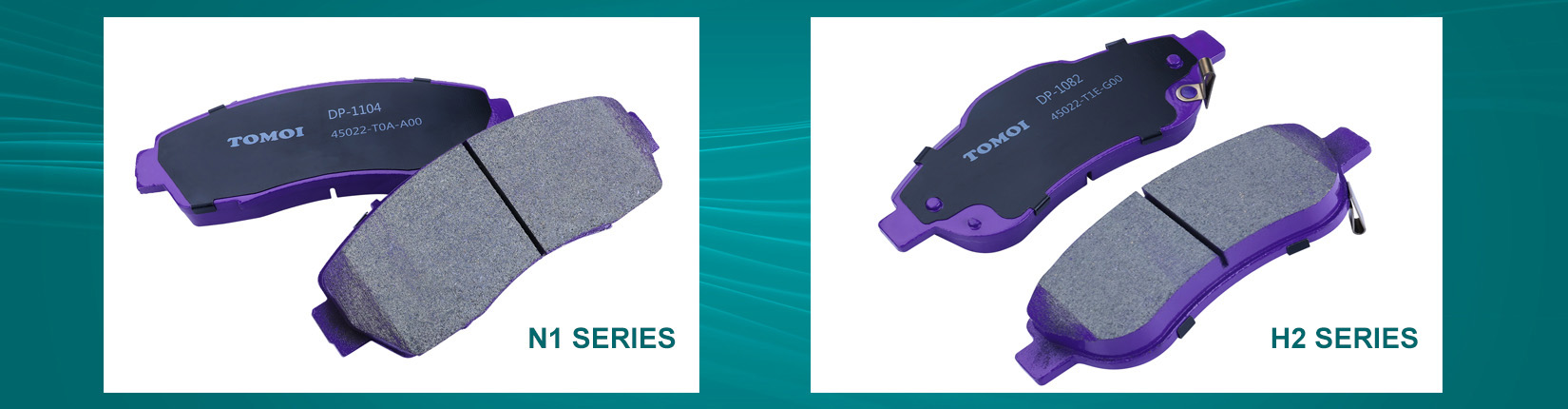
TOMOI N1 series Drum brake pads
TOMOI N1 series Drum brake pads use a special ceramic formula.and the friction material layer is composed of ceramic fiber, aramid fiber, carbon fiber, copper fiber, high-purity graphite, potassium titanate and resin. The specified friction coefficient is 0.36, which allows for short braking distance, high temperature resistance, less dust, no noise and long life-span.
TOMOI H2 series Drum brake pads
TOMOI H2 series Drum brake pads High-grade ceramic formula: The formula primarily includes ceramic fibers, aramid fibers, copper, high-quality resins, and other environmentally friendly raw materials.
Extremely stable friction coefficient, excellent noise reduction performance, ultra-low wear and minimal dust, good braking effect and comfort. Durable, high temperature resistant, low hardness of raw materials, high purity, non-damaging to brake discs, Scientific and reasonable processes that cover automated batching, weighing, and feeding ensure uniform and stable product quality.

TOMOI Brake Pad Strengths
■ TOMOI brake pads adopts the international advanced ultra-quiet ceramic formula, which effectively solves the problems of noise and dust.
■ TOMOI disc brake pads with FF level international standard friction coefficient, low noise, less dust, good braking effect.
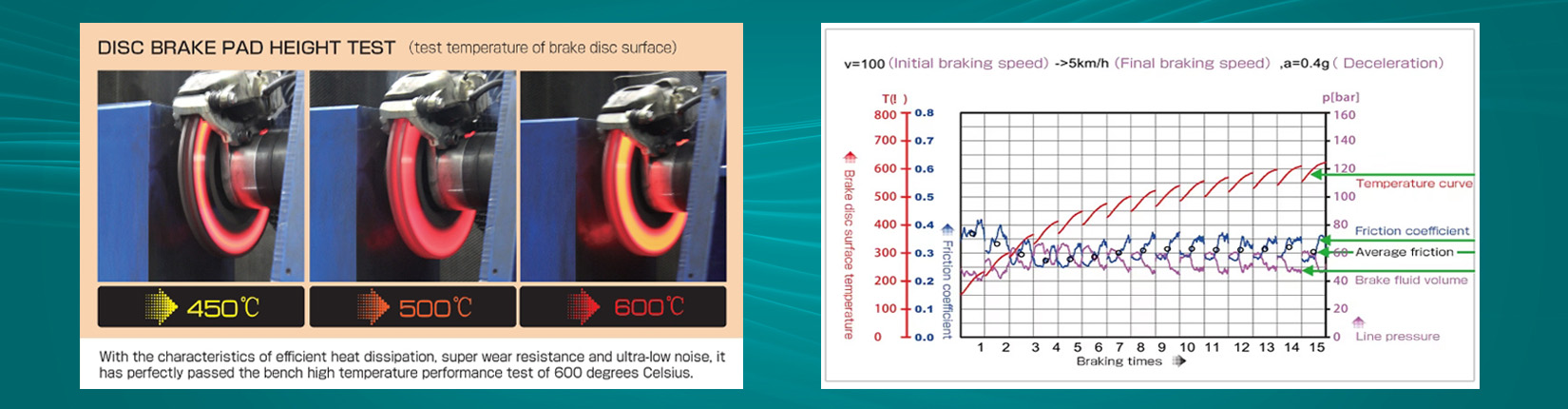
■ The high-temperature braking ability of TOMOI disc brake pads is outstanding, Under the high temperature conditions such as continuous emergency braking and downhill braking, the friction coefficient is stable and the braking effect is good. During the actual measurement cYunan Road testing ,after 20 consecutive prolonged braking actions the temperature of the brake disc/bad reached more than 570 degrees, but it still remained in good condition .
■ TOMOI disc brake pads use advanced ceramic formula and manufacturing process, which has the advantages of long life-span and wear resistance and can prolong the life-span by more than 25%.
■ There is more than 3000 kinds of brake pads in TOMOI, meets meeting various worldwide car models request.

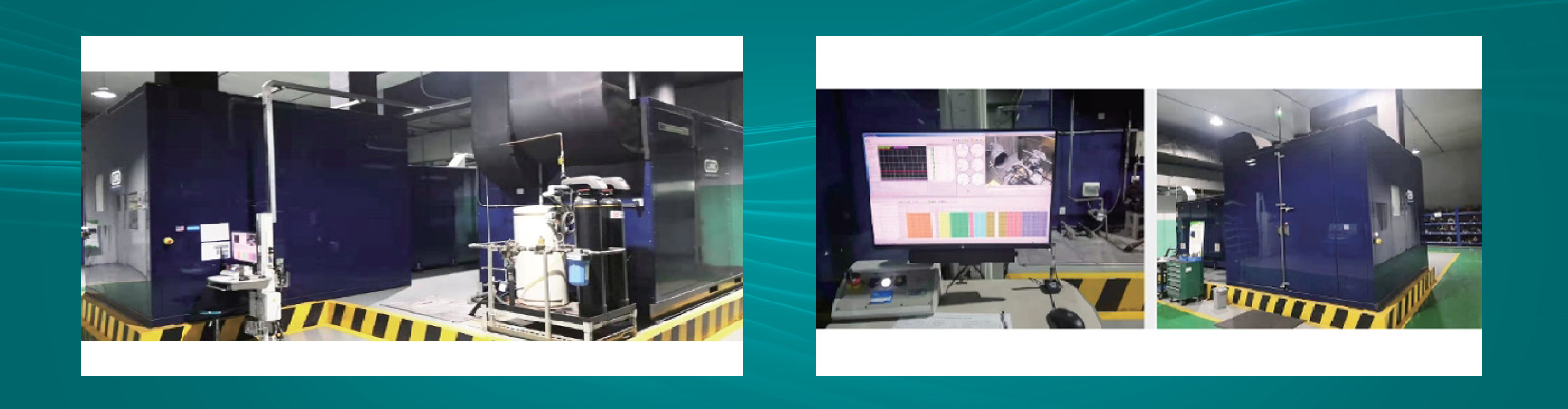
TOMOI Strict Testing
■ TOMOI brake pads undergo thousands of hours of cycle testing on the LINK 3900 Benching testing machine, TOMOI brake pads have advantages of wear resistance ,thermal stability and low noise frequency.

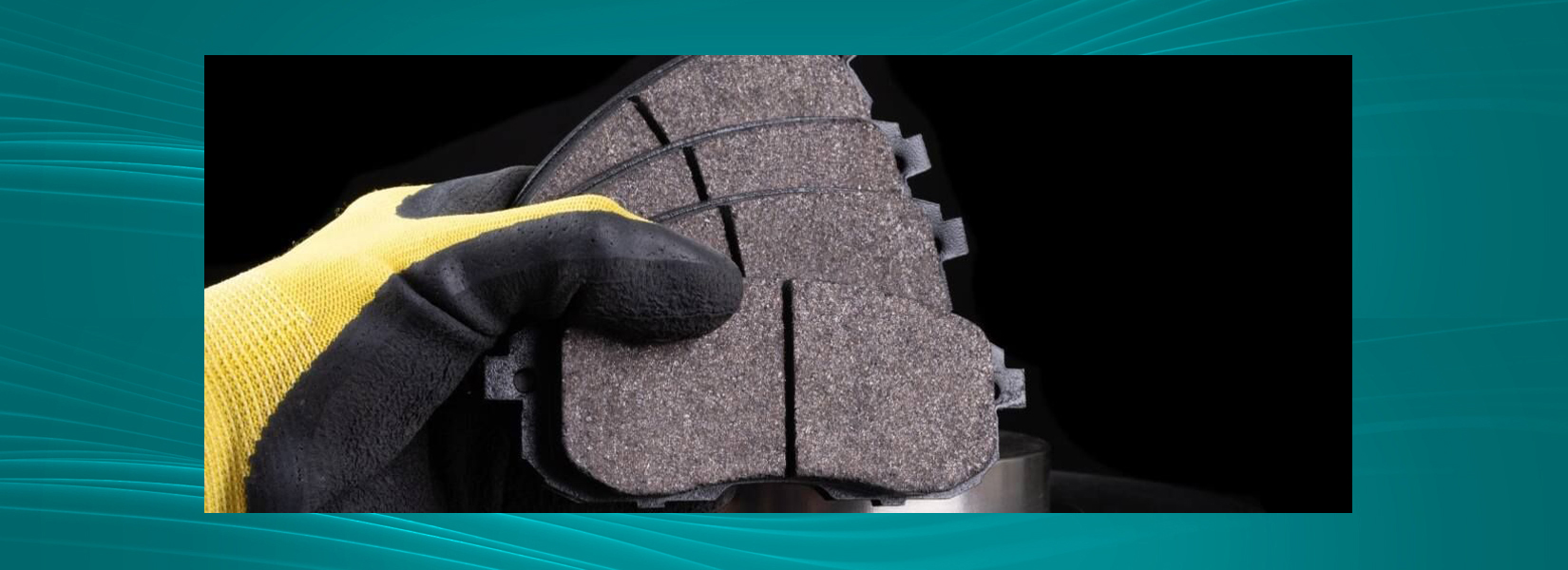
Brake Pad Structure
■ Structurally, brake pads are composed of friction material, bottom material Layer, viscose, steel back, muffler plate and accessories.

■ Note: This picture is for reference only. The structure of matching products may vary depending on the vehicle model.
■ Primer layer: Improves bonding performance, reduces heat conduction, maintains consistent compressibility for thinner friction plates, reduces noise, attenuates high-frequency squeal and couple attenuate vibration.
■ Friction material: The body material (abrasive+ lubricant, determines the friction coefficient and friction performance. The filer can reduce the cost and improve the ease of production. The binder can effectively bond various components and strengthen the fiber to enhance the mechanical strength.
Performance indicators related friction materials
1.The coefficient of friction is the ratio of the frictional force between two surfaces to the vertical force acting on one surface. This coefficient is one of the important indicators to measure the braking effect of brake pads.
2.Friction Level
■ EE grade: 0.25-0.35 is suitable for European and American cars .brake pads are relatively large and the friction coefficient is relatively low.
■ FF grade: 0.35-0.45 international standard friction coefficient.
■ GG grade: 0.45-0.55 for European models.
■ HH grade :0.55-0.65 for racing cars.
3.The higher the friction coefficient, the greater the friction force and the shorter the braking distance under the same braking force. But it is not that the higher the coefficient of friction, the better. Excessive friction coefficient will affect the comfort of driving. Such as the phenomenon of car nodding, Therefore, a balance point is desirable needs to be taken between the braking distance and friction coefficient.

Cautions:
■ Brake pads are an important part of vehicle’s braking system. Their life-span is determined by factors such as differences in driving habits vehicle models, road conditions, slope differences, private cars or taxis, etc. please carry out maintenance in accordance with the vehicle maintenance manual.
■ New change brake pads make low-speed brake noises. In fact, the original brake pads have caused wear on the brake discs after use, causing the new pads and the old discs to easily rattle. The complete solution is polishing the disc. the temporary solution is to polish the brake pads surface, Chamfer.
■ The size of the friction block of the brake pad manufacturers is inconsistent, especially the width. The maximum deviation between manufacturers can reach 3 mm, which causes the surface of the brake disc to look smooth but the standard size is installed, and the small one can easily make noise. How to fix: polishing brake discs.
■ There is a sudden noise after driving for a period of time. In this case, most of the time this is due to the fact that there are sand and gravel on the road between the brake pads and discs when braking. In this case, it is not only easy to make noise but also easy to damage the disc, but the foreign objects have fallen off after dismantling. In this case, only two of the four sides of the disc are damaged, and one of them is easy to see. How to fix: remove foreign objects, re-install the car.
■ No matter whether you step on the brake or not, there is a rattling sound, which may be because the brake accessories are not installed properly. How to fix: fasten accessories, re-install.
■ lf there is sound, the brake pads are in a semi-slip state at the moment of starting, so that the automatic transmission car has a unique sound, and there is no manual transmission. This kind of sound is a normal phenomenon when the brake pads are in a semi-slip state.
Maintenance Tips:
■ When to replace brake pads? You need to check the thickness. A new brake pad is generally around 1.5cm thick. With use, the thickness gradually decreases due to friction. When the thickness of the brake pad is visually reduced to about one-third of the original thickness.
- (approximately 0.5cm), the owner should increase self-inspection frequency and prepare for replacement.

■ For replacing brake pads, you need a series of tools including a jack, appropriate socket wrench, professional dis-assembly tools, and lubricants. Some tools like the jack and the crass socket for tire removal are usually provided with the vehicle, while professional tools may need to be purchased separately.
■ Before starting dis-assembly, slightly loosen the securing bolts of all wheels without removing them completely. This can utilize the tire’s friction with the ground, making the bolts easier to loosen. Next, use a jack to lift one side of the vehicle at the designated lifting points,usually located behind the front wheels and in front of the rear wheels on the vehicle’s structure.
■ The brake wheel cylinder of disc brake is typically secured to the cylinder bracket with two bolts. The cylinder bracket itself is connected to the oscillation bearing with two additional bolts, Therefore, when replacing brake pads, you only need to remove the two bolts securing the brake wheel cylinder.
■ Lubrication during maintenance: Apart from the contact points between the brake pads and brake disc, which do not require lubrication, other sliding and rotating parts should be appropriately lubricated. Specifically, the contact points between the brake pads and the calipers as well as the pins between the calipers and the brake wheel cylinder, need to be lubricated.
■ Remove the noise reduction shims from the brake pads, open the anti-squeal paste, and apply a quarter of the paste evenly on the steel back. Re-install the noise reduction shims afterward.
■ Pay attention to driving habits, reduce sudden braking and prolonged braking, and avoid drastic speed changes. Additionally, minimize risky driving behaviors like overloading and speeding to decrease the frequency and extent of brake pad wear.
■ Regular inspections: Generally, car owners can have the brake pads checked for wear each time when vehicle repairers change the oil. After some mileage, owners can also inspect the brake pads themselves. If the brake pads have been worn to the specified limit, they should be replaced promptly.
■ Regular cleaning: During daily use, brake pads are affected by factors like road dust, mud, sand, and moisture, which can cause adverse effect on their friction performance. Regular cleaning can maintain good friction performance and extend the brake pads lifespan.
■ Choosing the right brake pads: There are various types of brake pads available on the market, such as metallic ceramic pads and organic carbon brake pads. Owners should choose brake pads suitable for their driving habits and environment to ensure the braking system functions properly.

