
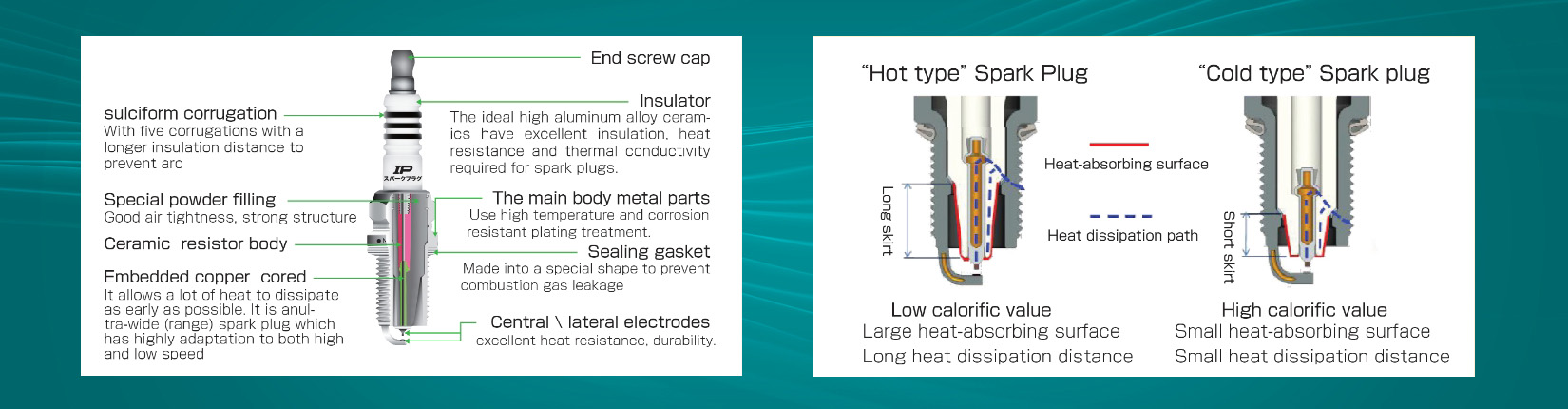
Spark Plug Introduction
The spark plug, an important component of the gasoline engine ignition system, introduces high-voltage electricity into the combustion chamber and then skips the electrode gap to generate sparks, resulting in igniting the combustible mixture in the cylinder. it is mainly composed of terminal nut. insulator, terminal screw, center electrode, side electrode and shell. The side electrodes are welded to the housing.
On the one hand, the spark plug has to withstand the sharp temperature shock, pressure shock and chemical corrosion in the combustion chamber at all times. On the other hand. it also has to withstand at least 30,000 volts of ignition high-voltage pulses. Therefore, spark plugs are required need to have good mechanical, electrical and chemical properties throughout their life cycle.
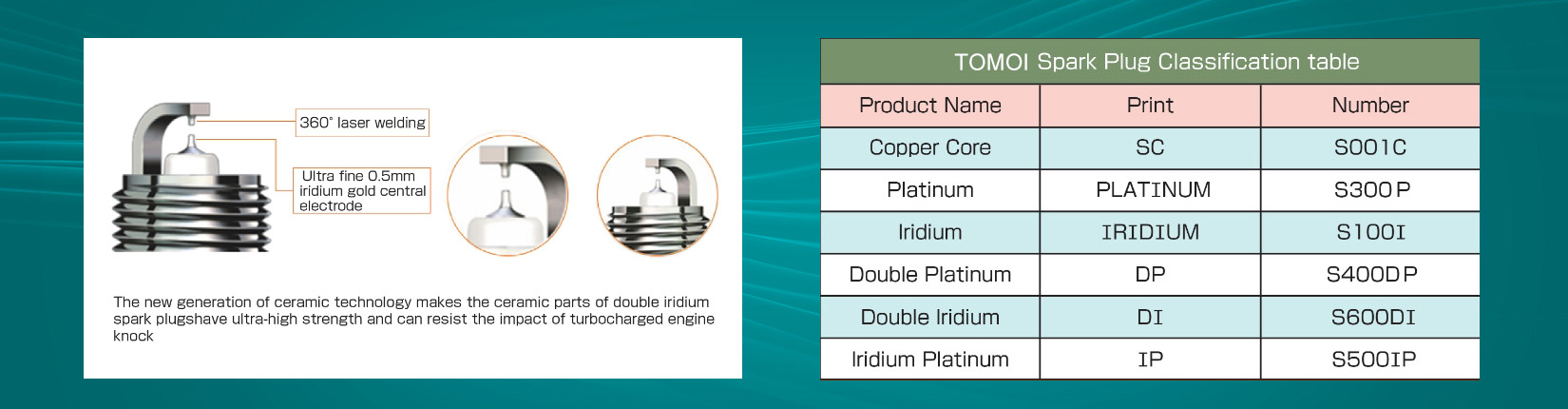
TOMOI boasts of hundreds of spark plugs in six categories. Nickel Alloy, Single Platinum, Single iridium, Double Platinum., Double iridium and iridium Platinum. The complete variety can be adapted to most of the world’s mass-produced brand cars.
Copper core nickel alloy spark plugs
The nickel electrode head embedded in the copper core can greatly improve the heat dissipation performance of the spark plug and effectively prevent the engine from overheating.
Single platinum spark plugs
After starting, the self-cleaning temperature can be felt faster, helping to improve the stability of the electrode gap, avoiding engine flame out caused by excessive clearance or and carbon deposition and carbon deposition and power shortage caused by too small clearance.
Single iridium spark plugs
It improves ignition efficiency, making the acceleration it more powerful to accelerate, reducing fuel consumption, increasing power and extending service life.
Dual platinum spark plugs
It improves ignition and flash over properties, stabilizes it in the temperature range between Self-cleaning and red-hot combustion, and has excellent durability and stability.
Double iridium spark plugs
It has better performance in terms of ignition ability, starting performance, acceleration performance, fuel economy and longevity.
iridium platinum alloy spark plugs
With the advantages of significant ignition efficiency, excellent acceleration performance, reduced fuel use and strong power, platinum can better withstand the high temperature in the cylinder, and the heat dissipation, durability and stability performance have been are maximized.

Double iridium Product Advantages
■ With the 0.5mm tip electrode design, second-generation dual iridium spark plug contributes to the rapid generation of flame cores. Therefore, the lower ignition voltage makes it more energy efficient.
■ Super acceleration performance: under simulated conditions, namely 0- 150KM/h acceleration, the time required tor double iridium spark plugs is 0.7 seconds faster than platinum spark plugs and 0.5 seconds faster than iridium spark plugs.
■ Instant start: it facilitates the cold start of the car, provides greater efficiency in cold weather and cold regions, and reduces voltage amplitudes.
■ More fuel saving: The second generation double iridium spark plug has the advantages of easier ignition, more complete combustion, higher energy conversion rate, less exhaust emissions, and more environmental friendly.
■ Super long life: When the engine ignites, the instantaneous temperature in the cylinder is as high as 1500℃ to 1800℃. The melting point of the second-generation double iridium is as high as 2454℃, The product life can reach more than 1 00,000 kilometers.
■ A new generation of ceramic technology endows the ceramic parts of the dual iridium spark plug with high strength, making it resistant to the effects of turbo engine knocking.
Performance requirements for spark plugs
■ Mechanical behavior:
The ceramic and electrode materials of the spark plug should have sufficient mechanical strength to withstand the impact of the explosion pressure of 80 bar. At the same time, they are required to be able to withstand the alternating shock of inhaling gases as low as minus-40’C and combustion gas temperatures as high as 2500’C.
■ Electrical performance:
The ceramic of the spark plug is required to withstand at least 30KV ignition high voltage pulse impact without being broken down. And there should be no flash over creepage on the surface of the ceramic.
■ Chemical properties:
Ceramic and electrode materials are required to withstand chemical corrosion by combustion products (compounds of PbPS). The choice of spark plug calorific value must match the engine. improper matching of calorific value may occur in two situations: the melting of the ceramic or electrode after the spark plug is overheated, resulting in carbon deposition due to over-cooling. As shown below.Too high calorific value leads to carbon deposition.The calorific value is too low to cause overheating. When you choose a spark plug, in addition to confirming the thread specification and the size of the ignition end, you must also choose a spark plug with a suitable calorific value!
■ Carbon deposition resistance:
The anti-carbon performance refers to the ability of the spark plug to resist the failure of carbon deposits under low temperature or low speed operating conditions (such as speed less than 40km/h). It is usually tested by multiple repeated starts of the vehicle in low temperature conditions. The factors that affect the carbon deposition performance mainly include the following aspects:
A.Mixed gas concentration: it is determined by the ECU number. Under the conditions of low speed and small load. the mixed gas is too rich to form carbon deposits.
B.Driving habits: f the vehicle runs at low speed and low road for a long time. it will cause serious carbon deposition.
C.Fuel quality: Inferior fuel cannot be fully burned and easily forms carbon deposits.
D.Spark plug temperature: The spark plug will continue to produce carbon deposits when the operating temperature is below 500℃.
E.Spark plug skirt structure: Optimized ceramic skirt and top structure can effectively reduce carbon deposits.
Common Problems of improper Installation
■ Ceramic cracks, hexagonal damage
■ Excessive torque can cause the thread to crack or break.
■ The washer is not deformed due to too little torque, and the electrode is overheated and fractured.
■ There is a corresponding specification for the installation sleeve of spark plugs, namely ISO 11168:95, it’s worth noting that the original specification was for a spark plug hex minimum size of 1 6mm, which does not apply to 14mm spark plugs. Therefore, it is recommended that the latter be designed with reference to the 16mm specification to avoid damage to the ceramic during installation.

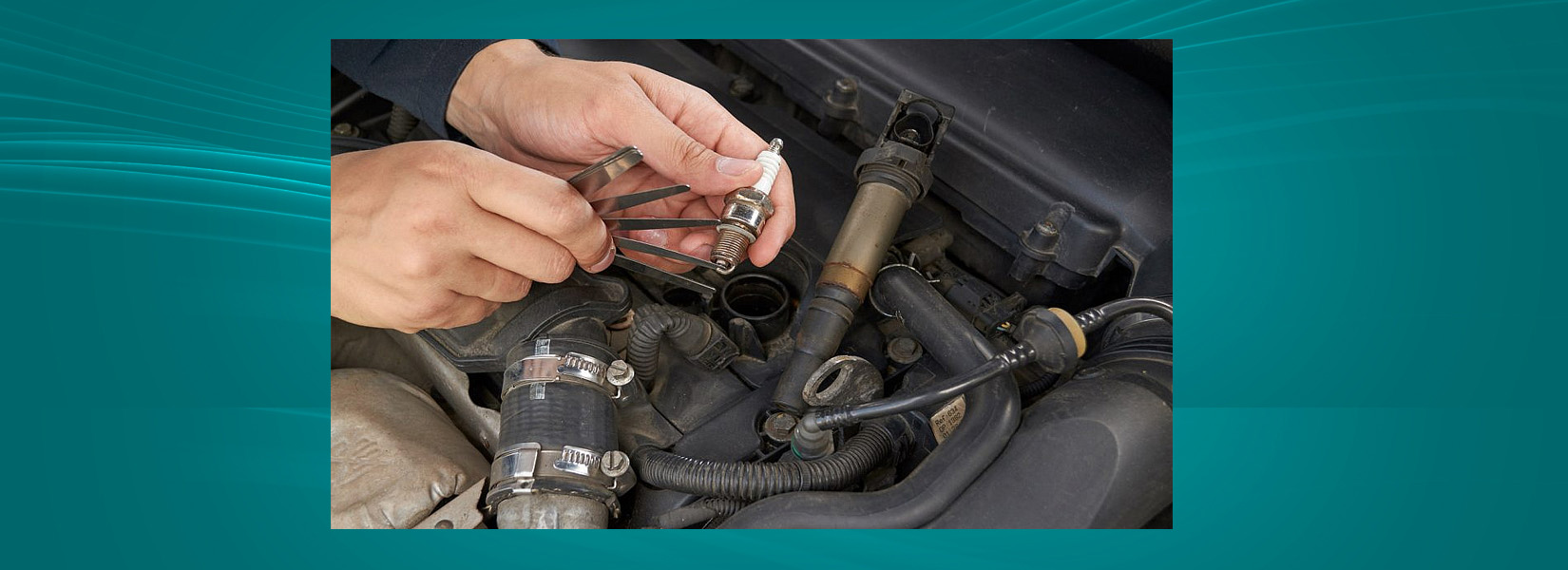
Six Steps for Repair and Installation
1.Remove the dust around the terminal cap of the high-voltage wire, or use a high-pressure air gun to remove the dust and dirt around the spark plug to prevent the dust or dirt from falling into the combustion chamber or the outer gasket seat.
2.Pull out the high voltage connection cap by hand or auxiliary tool. Never unplug the high-voltage wire directly to prevent the high-voltage wire from separating from the contacts in the wiring cap.
3.Loosen the spark plug with the special sleeve. The sleeve must match the size of the hex face of the spark plug.Then, it can be gently unscrewed with fingers or with the help of a special rubber tube.
4.Gently screw the new spark plug into the cylinder head. It can be screwed in with a rubber tube or a magnetic sleeve if the mounting hole is deep. Do not throw the spark plug directly into the mounting hole to avoid damage to the ignition end.
5.Check whether the high-voltage terminal cap is aged or damaged. Then hand press the high voltage terminal cap vertically onto the spark plug until a click is heard. It is recommended to replace the spark plug, high voltage wire and ignition coil at the same time.
6.Tighten the spark plug to the recommended torque, or follow the installation instructions to an angle. The socket size must match the hex. The internal aperture should be large enough to avoid stressing applying too much stress to the ceramic.

Spark Plug Inspection and Maintenance
Spark plugs are wearing parts and are generally not used after their lifespan expires. Some manufacturers stipulate that the spark plug can be manually adjusted after use for a period of time before use. For this case, please note that:
■ Some manufacturers stipulate that the spark plug can be manually adjusted after use for a period of time before use. For this case, please note:
■ Check the spark plug electrode for ablation and measure the gap with a feeler gauge. If the gap has exceeded the specified range, you can hold the spark plug with the ignition end vertically downward, and tap the side electrode on the table lightly.
■ Excessive force will lead to excessive deformation of the side electrodes, resulting in a small gap. At this time, the side electrode needs to be slightly broken outward with needle-nose pliers, Do not let the needle nose pliers touch the ceramic.
■ If there are serious the ceramic carbon deposits on the working end of the spark plug. the spark plug cannot be used again. It is absolutely not allowed to directly burn the ignition end of the spark plug with an open flame to remove carbon deposits, because heating with an open flame will cause cracks in the ceramics.

